In this section, you will examine a number of topics related to mobile and wireless security. You will learn about specific security issues related to wireless networking and mobile devices.
Concepts: Security has always been a challenge in networking. Wireless networking and mobile devices make achieving network security more complex.
Objectives: The objectives of wireless networking and mobile security are similar to those of conventional network security—to protect the network, devices, and data from harm.
Context: The information and communication fields have experienced momentous changes over the past few decades. Learning about these changes will help you meet the challenges of securing wireless networks and mobile devices.
Technology: The evolution of technology has deeply impacted the way information is secured. You need to recognize how ongoing developments in technology continue to present both challenges and opportunities in wireless network and mobile device security.
Understanding: Wireless networks and mobile devices are pervasive in today’s society. You will come away from this course with a firm understanding of how security is achieved for mobile devices and wireless networks.
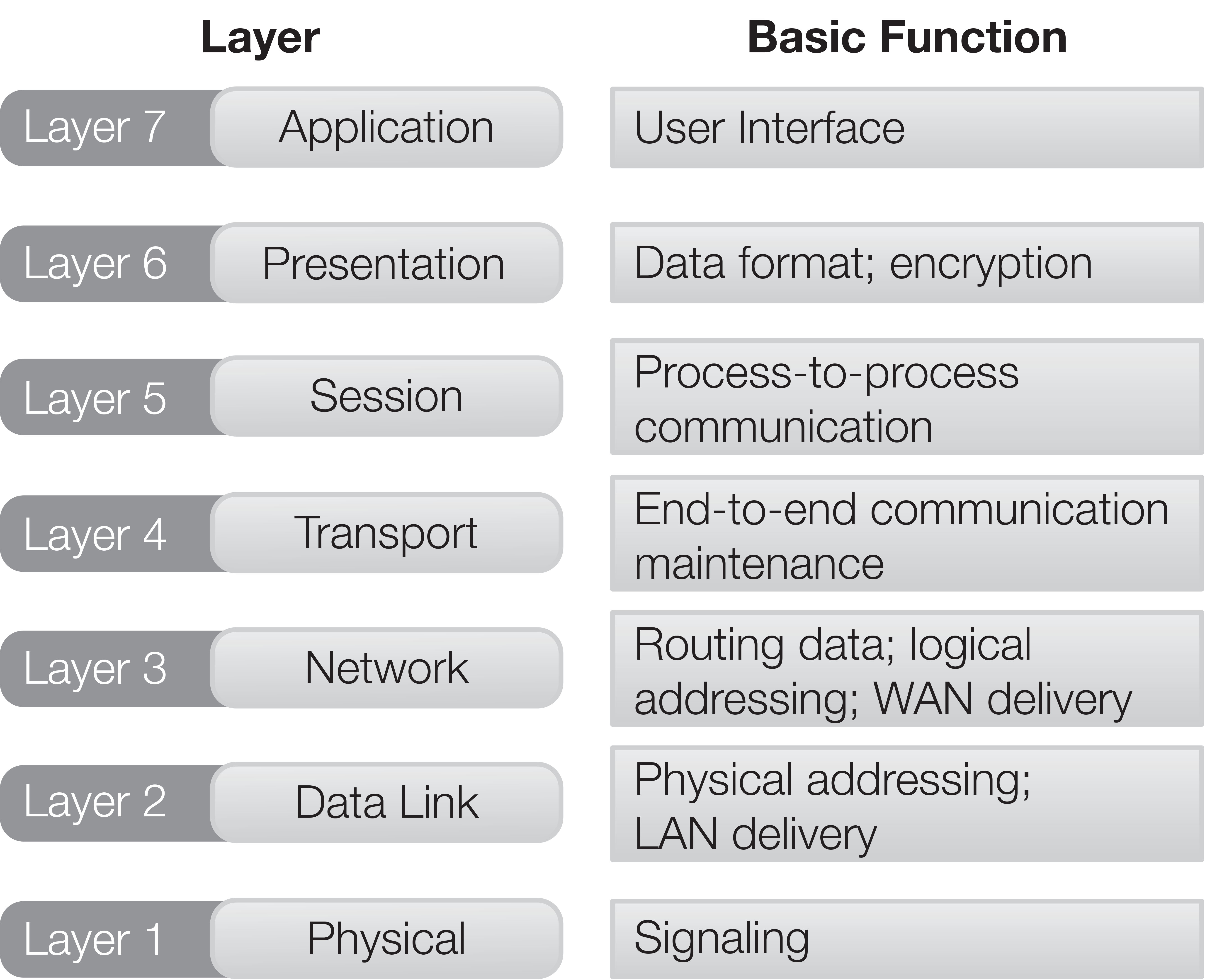
The answer was to develop a model that defined standards for communication protocols and the physical and logical interfaces between machines and subsystems. Published by the International Organization for Standardization, the OSI Reference Model defines seven layers (referred to as a stack) that describe standards from the physical wire all the way up to the application interfaces on computers. Each layer has a specific function, common among all devices, and a specific way of communicating with the layer above and the layer below in the stack.
This standardization enabled different companies to produce solutions or products that were compatible with products from other manufacturers, even without up-front collaboration. This led to innovation and more products.
The OSI Reference Model benefitted consumers—businesses, universities, and governments—who enjoyed greater choice. This helped propel the networking industry into the economic power that it has become.
Click on each of the following topics to learn more. Next, click the ACTIVITY button to complete a brief exercise.
- The seven layers of the OSI Reference Model
- Communicating over a network
- The Data Link Layer
- The Physical Layer

Click on each topic to learn more. Next, click the ACTIVITY button to complete a brief exercise.
- The effect of the FCC decision
- Standards for WLANS

The first wave of the wireless revolution included early adopters who provided fixed-line PC-based Internet services at cafés and shopping malls. Their fee-based services, which were fraught with security issues—including keyboard sniffers to capture passwords and banking details—soon succumbed to free public wireless broadband offerings.
Soon, it became common to have high-speed ADSL and broadband fixed-line networks in homes. To reduce churn, ISPs often supplied Wi-Fi–enabled gateways to consumers. These measures helped Wi-Fi gain traction in homes and small businesses. In 2005, wireless broadband accounted for productivity gains of $28 billion.

Wireless fundamentally changed the way some industries did business. A few of them are discussed here.
Click on each industry to learn more.
- Health care
- Warehousing and logistics
- Retail
- General business and knowledge workers
Click on each topic to learn more about each one. Next, click the ACTIVITY button to complete a brief exercise.
- The Wi-Fi market
- How Wi-Fi affects developing nations
- The Internet of Things
In this section, you will have an opportunity to practice the concepts and processes that you have explored in this lesson.
The Demo Lab provided in this lesson guides you through the steps needed to perform tasks related to wireless and mobile device security. You may review these guided interactions as many times as needed.
The Hands-On Lab provides you with an engaging learning experience that is diagnostic and flexible. Follow the instructions provided in the Lab Manual.
In this section, you will have an opportunity to use what you have learned in this lesson to meet a challenge. A scenario is provided here that depicts situations often faced by professionals in the workplace.
You will explore the scenario, review related critical information, research a topic, and present your findings. Complete your work by submitting the graded assignment.
You work as a networking consultant for Secure Systems Solutions (SSS). You specialize in wireless and mobile device security.
The IEEE is in the process of ratifying the specifications for 400 Gb Ethernet. You recently attended a meeting about how these new specifications may affect your clients.
You receive an e-mail message. You can see that it is from your boss, Claire.
The new specifications for 400 Gb Ethernet will have a big impact on our clients. I think it’s important that we stay abreast of the developments from the Ethernet Alliance and the Ethernet Alliance 400GbE Subcommittee.
Please research the progress they are making. Then write a report that describes the Ethernet Alliance’s goals, how they plan to achieve those goals, and their timeline.
Thanks in advance for your hard work.
Claire
Senior Manager, SSS
In this lesson, you learned about networking and the Open System Interconnection Reference Model and its Data Link Layer, which has been dominated by the Ethernet protocol for decades.
Research the progress the IEEE is making in ratifying standards for 400 Gb Ethernet. Then write a report that describes the Ethernet Alliance’s goals, how they plan to achieve those goals, and their timeline.
For a checklist of action items, navigate to Course of Action on the right panel of the screen.
Use the following checklist as a guide to complete this assignment. Note that the tasks you have completed are already checked on the list.
Tasks
- Read the verbiage of the e-mail from your boss.
- Consider all the factors that contribute to the challenge.
- Research the progress the IEEE is making in ratifying standards for 400 Gb Ethernet.
- Write a report that describes:
- The Ethernet Alliance’s goals
- How the Ethernet Alliance plans to achieve those goals
- The timeline for ratifying standards for 400 Gb Ethernet