Legal Issues in Information Security
Privacy Overview
Think about the answers to the following questions and then click each question to reveal its answer. Next, click the ACTIVITY button to attempt a simple activity related to privacy.
- What is privacy?
- Why is privacy an issue?
- What is the difference between information security and privacy?



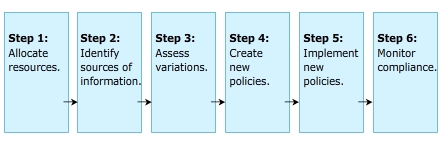
Position the mouse pointer over each step to learn more. Then, click the ACTIVITY button to attempt a scenario-based activity.






Allocating
Identifying
Evaluating
Creating
Implementing
Monitoring
Click each role to learn more.
- Legal Officer
- Information Technology Officer
- Senior Management
- Chief Information Security Officer
- Chief Privacy Officer
Review the following characterization of public versus private information. Can you think of other types of private or public information? Try categorizing the type of information as public or private. Then, click the ACTIVITY button to answer a simple question on categorization of information.
Private Information
Social security numbers
Financial details
Health information
Biometric data
Criminal history data
Public Information
Birth and death certificates
Minutes of meetings of government agencies
Real estate filings
Sex offender registration lists
Court records
With regard to privacy in a world where the Internet is so much a part of our lives, the importance of privacy laws is quite evident. Let us look at some important privacy laws. Click each privacy law given to review its importance. Then, click the ACTIVITY button to attempt a simple activity related to privacy laws.
- The Fourth Amendment to the Constitutional Law
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
In this section, you will have an opportunity to practice the concepts and processes that you have explored in this lesson.
The Hands-On Lab provides you with an engaging learning experience that is diagnostic and flexible. Following the instructions provided in the Lab Manual, you will be able to practice the steps IT Security Specialists perform on a daily basis and develop the skills required for effective execution and management of IT Security operations.
In this section, you will have an opportunity to apply what youíve learned in this lesson in the context of analyzing a business situation. Although simplified, a problem scenario provided here depicts the challenges often faced by professionals in the workplace.
In this interactive case study, you will explore a business situation, review critical information related to the problem discussed in the case, decide on the course of action, and receive a decision analysis summary that discusses the implications of your decision. Once you analyze the impact of your decision, explore alternative solutions to learn about other potential ways to address the issue in the case. Complete your work on the case by submitting the graded assignment that will reflect on your process of analyzing the business situation and defining an appropriate course of action.
You meet the chief security officer of your company for the discussion on the next steps. Click the image of the chief security officer to find out what happens next.
After you have gone through the challenge, navigate to Contributing Factors from the panel at the top of your screen.We have planned another meeting next week, where the board will finalize the remedies to implement in the systems. So, the board wants you to create a summary that supports your list of suggested remedies. I will send you an e-mail that will detail what all is required in your summary.

Ask a Consultant

Review Documents

Read E-mail
Select the icon from the top to receive additional
information related to the situation
Tasks
- Discuss with the chief security officer.
- Consider all the factors that contribute to the challenge.
- Review the case of the Department of Veterans Affairs.
- Analyze the mistakes of employees and the Veterans Affairs Administration.
- Create a summary, in a bullet-point list, of all the suggested remedies.
- Write your rationale for each suggested remedy.
- Prioritize your suggested remedies for the given challenge.
- Write your final recommendations
- Do a self-review of the executive summary with respect to the evaluation criteria mentioned in the assignment requirements.
- Submit the assignment to your instructor.