Network Security,
Firewalls, and VPNs
Network Security Implementation Strategies
Network Security Implementation Strategies
Network Security Concepts
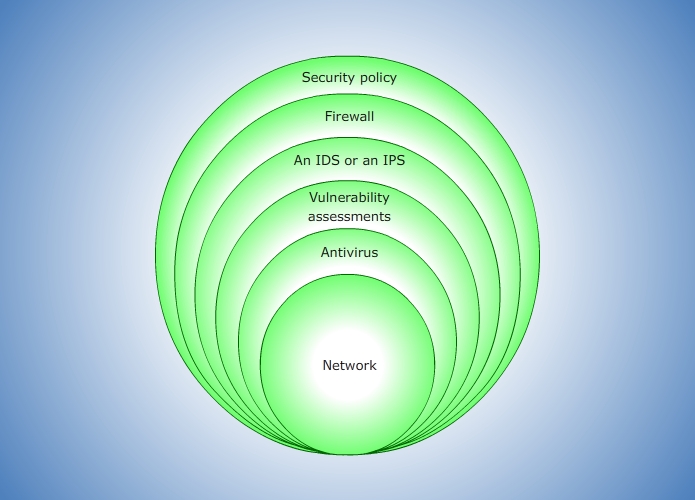
Irrespective of its size, purpose, or function, network security is applicable to all organizations. Network security includes layered defenses, proper use of protocols, use of addressing for segmentation, communication management, and system hardening.
Think about answers to the following questions related to network security. Then, click each question to reveal its answer.
Think about answers to the following questions related to network security. Then, click each question to reveal its answer.
- How does layered security improve security?
- How does layered security improve network security?
- What are the various types of IP addresses used in a network, and how do they affect security?
- What are the different types of addresses used in a network, and how do they affect security?


System Hardening
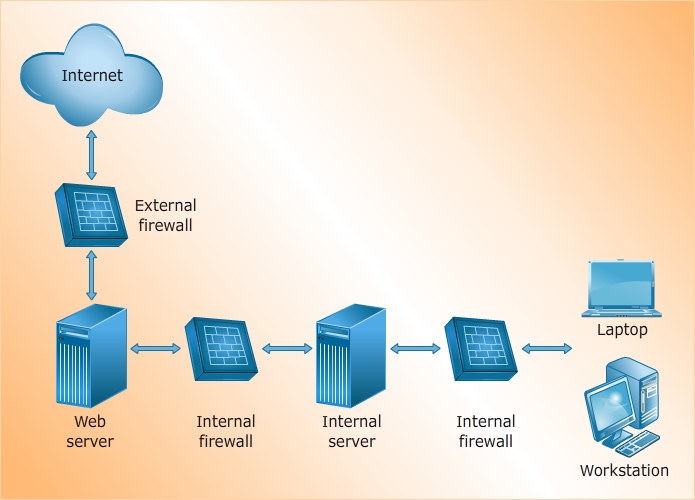
System hardening focuses on improving the security of hosts and nodes. The system hardening process reduces the attack surface of a potential target by removing unnecessary components and adding protections. Review the system hardening methods given below. After going through the system hardening methods, click the ACTIVITY button to attempt a simple activity.
The system hardening process involves installing application and operating system updates and patches, using strong passwords, restricting or prohibiting anonymous access, removing unneeded services, and separating the production and development environments, among other restrictive techniques.
Click here to know more about the system hardening techniques.
Click the RESOURCES icon to view examples of resources available for hardening systems and descriptions and links to hardening guidelines and standards.
Click here to know more about the system hardening techniques.
Click the RESOURCES icon to view examples of resources available for hardening systems and descriptions and links to hardening guidelines and standards.
Components of Security
To have a successful network security implementation, an organization should consider not only the bigger picture but also the individual aspects of security. The various components of security are listed below. Click each security component to review the role it plays in securing information systems in an organization. After going through the components of security, click the ACTIVITY button to attempt a simple activity.
- Node security
- Network security
- Physical security
- Administrative controls
Security Concerns for an Organization
An organization includes local, remote, and mobile hosts. Review the following scenario. After going through the scenario, click the ACTIVITY button to attempt a simple activity.
Elite Corp. is a retail company that deals with consumer products. It has the following types of employees:
- On-site users: Work primarily in company-owned facilities
- Field users: Work off-site at multiple locations
- Teleworkers: Work from home
- Road warriors: Frequent travelers who work from multiple locations
- Roaming users: Work primarily in company-owned facilities but not always from the same desk or in the same cubicle
Success of Network Security
To have a successful network security implementation, the organization must enforce access control. To effectively defend against threats, the organization should be able to authenticate and authorize users. Additionally, the ability to log and monitor activity is crucial to success.
Think about answers to the following questions related to the success of a network security. Then, click each question to reveal its answer.
Think about answers to the following questions related to the success of a network security. Then, click each question to reveal its answer.
- What is the purpose of authentication in network security?
- What is the purpose of authorization in network security?
- What is the purpose of accounting in network security?
- What is the purpose of encryption in network security?




In this section, you will have an opportunity to practice the concepts and processes that you have explored in this lesson.
The Hands-On Lab provides you with an engaging learning experience that is diagnostic and flexible. Following the instructions provided in the Lab Manual, you will be able to practice the steps IT Security Specialists perform on a daily basis and develop the skills required for effective execution and management of IT Security operations.
You have been working on the network project of Corporation Techs. Your manager now wants to brief you about your next task, which is a continuation of the assignment based on the Corporation Techs scenario.
Click the image of the manager to get his instructions.
After you have gone through the challenge, navigate to Contributing Factors from the panel at the top of your screen.
Click the image of the manager to get his instructions.
After you have gone through the challenge, navigate to Contributing Factors from the panel at the top of your screen.
As part of improving the network security of Corporation Techs, you need to identify security concerns and risk mitigation strategies for Corporation Techs. To identify security concerns, you need to identify the networked technology used at home, at work, or as a personal convenience in Corporation Techs. All the best!
Contributing Factors
From where can you gather information on this case? Let's find out by clicking the contributing factors. After you have gone through the contributing factors, navigate to Course of Action from the panel at the top of your screen.

Review Documents
Research the Internet
Review Documents

Research the Internet
Select the icon from the top to receive additional
information related to the situation
Course of Action
Use the following checklist as a guide to complete this assignment. Note that the tasks that you have completed are already checked in the list.
Tasks
- Consider the advice of the chief security officer.
- Identify various devices on the network.
- Review various devices available on the network.
- Identify three potential threats to the node security of the device.
- Detail a risk mitigation mechanism for each threat.
- Explain why the risk mitigation strategy you suggested will work.
- Submit the final security concerns and risk mitigation strategy to the instructor.